PREMATURITY
- Druzycare
- Nov 17, 2024
- 3 min read
Premature or "preterm" babies are those born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. The baby's internal organs are still developing at this delicate period.
CATEGORIES OF PRETERM BABIES
A. Extremely preterm (babies born less than 28 weeks of gestation).
B. Very preterm (28 to 32 weeks of gestation).
C. Moderate to late preterm (32 to less than 37 weeks of gestation).
CAUSES OF PRETERM BABIES
1. Spontaneous causes: e.g., multiple pregnancy-threatening abortions, physical exertion, acute emotional stress, chronic and systemic maternal diseases or infections, maternal malnutrition, cigarette smoking during pregnancy, drug addiction, etc.
2. Induced causes: this usually happens when there is impending danger to the mother or fetus. E.g., maternal diabetes and severe heart disease, placental dysfunction, eclampsia, hypertension, foetal distress, antepartum haemorrhage, etc.
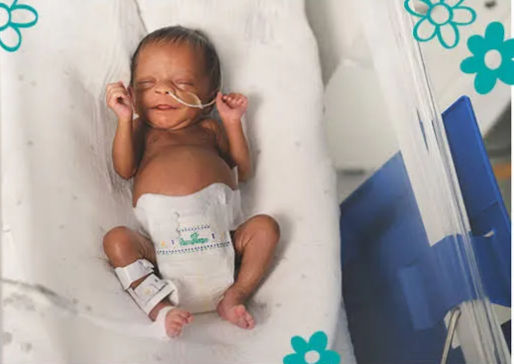
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PRETERM BABIES
A preterm baby is;
a). small in size with a relatively larger head than the body.
b). Skull bones are soft, sutures are widely separated, and fontanelles are large. Scalp hairs are scanty.
c). Eyes remain closed and protruding; ears are soft and flat.
d). Skin is shiny, thin, delicate, and pink, with plenty of lanugo hair.
e). The abdomen is full, soft, and round, with prominent veins.
f). Nails are short and not grown up to finger tips.
g). Deep creases over soles and palms are absent or less.
h). The genitals are poorly developed.
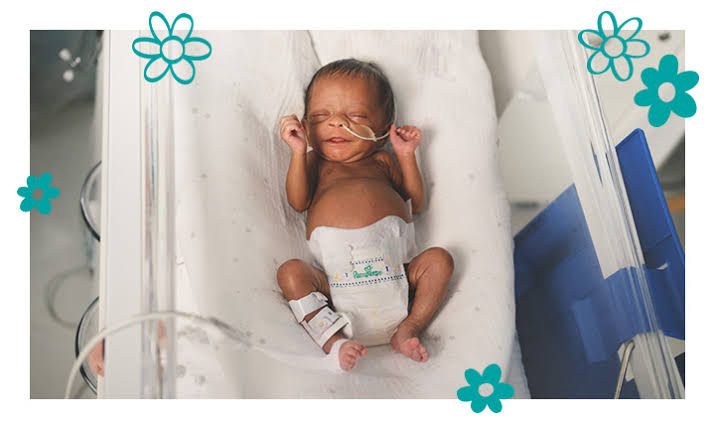
PROBLEMS OF PREMATURE
All problems of the preterm are associated with poor development of the organs and systems of the body.
a). Alteration of respiratory functions, i.e., breathing problems.
b). Immaturity of the central nervous system, e.g., poor sucking and swallowing reflexes, etc.
c). Disturbances of the circulatory functions, e.g., intracranial haemorrhage or bleeding.
d). Impaired thermoregulation: low body temperature (hypothermia).
e). Ineffective gastrointestinal and hepatic function: immature liver and abdominal distension, etc.
f). Metabolic disturbances: low levels of glucose, calcium, oxygen, and protein.
g). Highly prone to infections.
h). Impaired renal function: urination may be delayed.
PREVENTION
Prevention of preterm birth is important through early detection and management of high-pregnant women during antenatal care.
MANAGEMENT
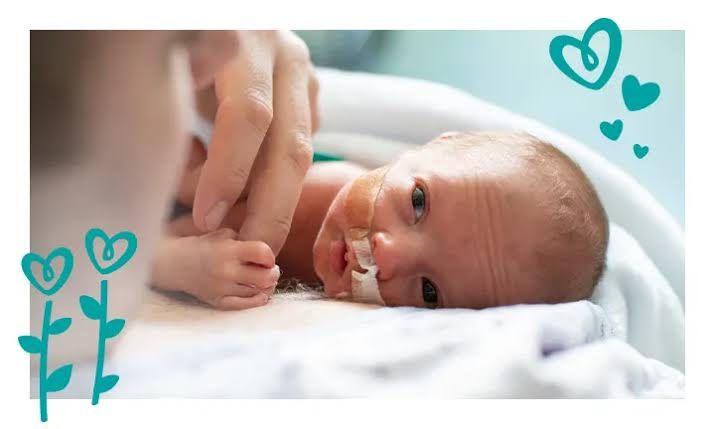
KANGAROO MOTHER CARE (KMC)
This is a low-cost approach for the care of preterm babies. It is a special way of caring that involves direct, continuous, and prolonged skin-to-skin contact between the mother and the baby and exclusive breastfeeding, thereby promoting their health and wellbeing through effective temperature control, breastfeeding, and bonding.
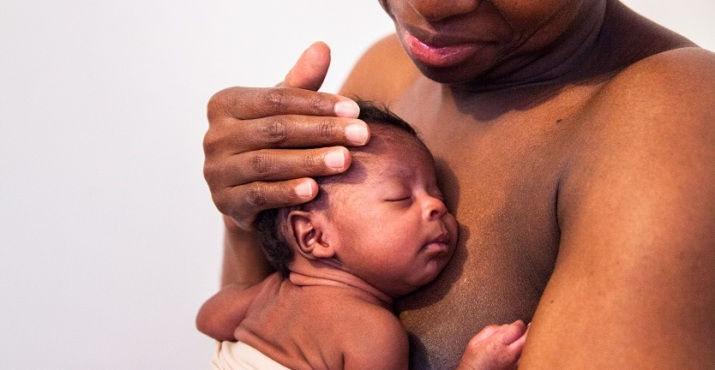
Benefits of KMC
1. It helps in temperature regulation and metabolism.
2. It helps the baby to be fed exclusively by the mother.
3. It helps the baby satisfy all five senses. I.e
Touch: the baby feels warm through skin-to-skin contact with the mother.
Hearing: baby listens to mother's voice and heartbeat.
Taste: The baby sucks the breast to feed.
Smell: babies perceive the mother's odour.
Vision: The baby makes eye contact with the mother.
4. A preterm baby has more regular breathing.
5. KMC prevents hospital-acquired infections.
6. It improves the mother-infant bond.
7. It improves the overall health of the baby.
KANGAROO MOTHER CARE PROCEDURE AND POSITIONING
Counsel the mother and the family members, explain the procedure, and answer any questions.
Mother should wear a front-open, light dress, as per local culture.
Baby should be dressed in a front-open sleeveless shirt, cap, socks, nappy, and hand gloves.
The baby should be placed between the mother's breasts in an upright position.
The baby's head should be turned to one side and in a slightly extended position, which helps to keep the airway open and allow eye-to-eye contact between mother and baby.
The baby's hip should be flexed and abducted in a frog-like position. The arms should also be flexed and placed on the mother's chest.
Baby's abdomen should be placed at the level of the mother's epigastrium.
The baby should be monitored for airway patency, breathing, colour, and temperature.
A mother should be supported in order to breastfeed her baby.
Mother should be supported psychologically.
Privacy should be maintained.
KMC should be initiated early once the baby is deemed fit and stable.
KMC can begin with one hour and increase to 24 hours to avoid stressing the baby.
The mother can sleep and rest with the baby in the KMC position.
Any other family members, including the father of the baby, can relieve the mother while she takes a break.
KMC should be continued after discharge at home until the appropriate weight is achieved.
Start Your Baby's Journal Today!
Begin capturing moments that will last a lifetime. Embrace the journey of parenthood and create a beautiful keepsake for your growing family. Purchase your Baby's Memories and Milestones Journal now and treasure those precious memories for years to come.
VISIT: https://selar.co/babyjournal.






Comments